Research fields
Optical Network
Optical packet/burst switching
Optical packet switched networks are emerging as a serious future candidate for the evolution of optical telecommunication networks to support high-throughput services such as voice over IP (VoIP) and high quality video streaming on demand. In an optical network with optical packet switches interconnected with optical fibers running wavelength division multiplexing (WDM), packets are transmitted from source to destination without any optical-electrical-optical (O/E/O) conversion.
Buffering at intermediate nodes is eliminated. The use of optical buffering through fiber delay lines (FDLs) to delay a packet for a specified amount of time while waiting for a future transmission may not feasibly to provide a large delay time.
Elastic optical network
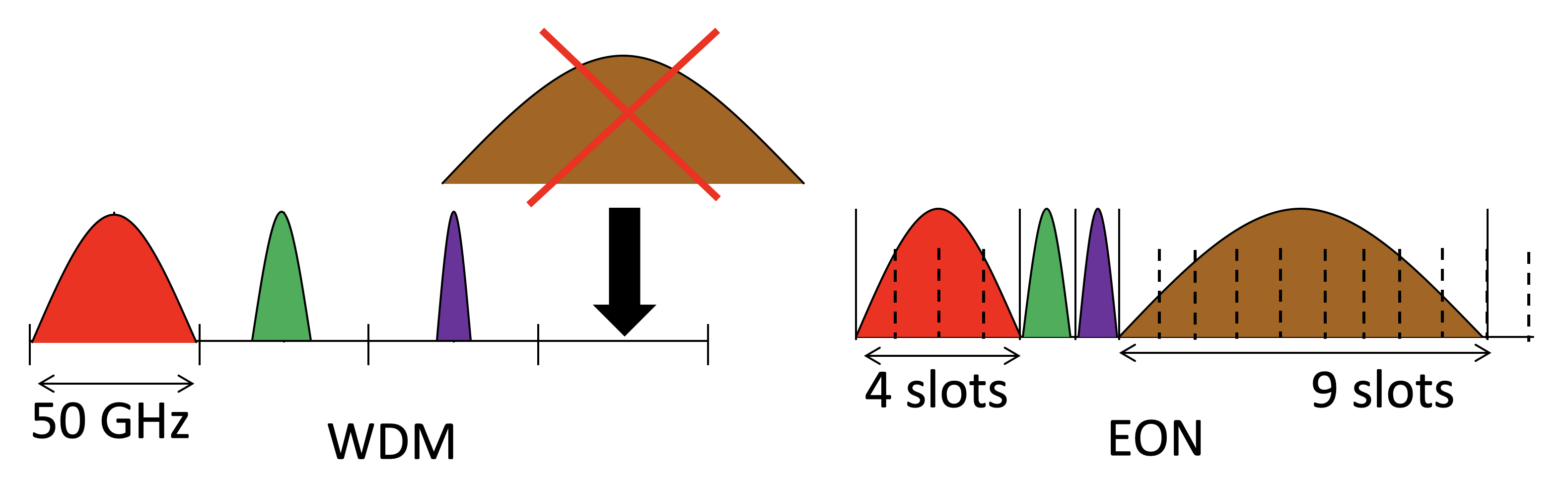
Elastic optical networks (EONs) provide spectrum slots that provide finer granularity compared to the channel spacing provided by the dense wavelength-division multiplexing (DWDM) optical networks. It can accommodate huge data rate traffic thereby increasing the network capacity.
A common issue in an EON is the bandwidth fragmentation problem which occurs because of dynamically setting up and tearing down of lightpaths. Because of the termination of a few lightpaths at different links of the network, it is possible that those terminated lightpaths are not continuous and contiguous. The lightpath request is rejected even though enough slots are available but the slots are non-contiguous.
Software Defined Networking
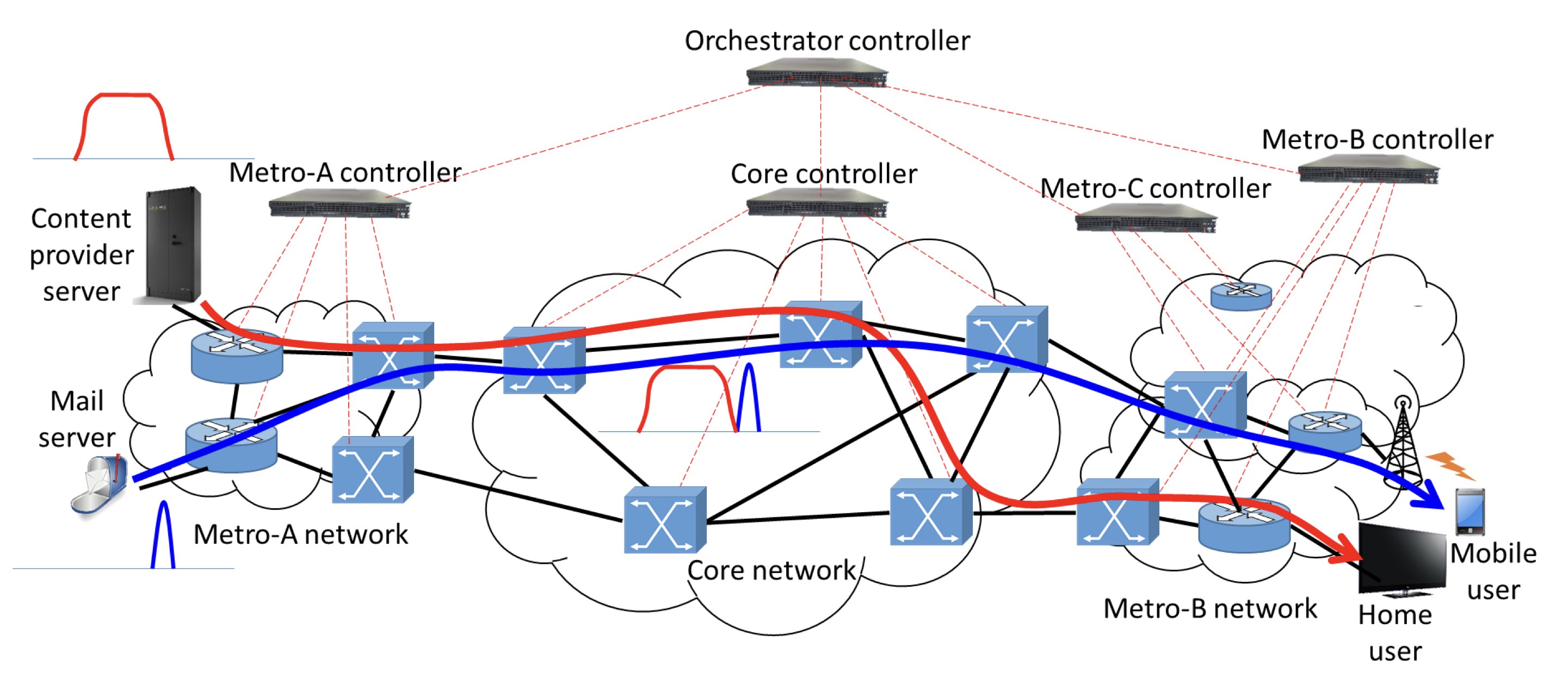
SDN separates the network control and data forwarding planes. This allows network engineers and administrators to respond quickly to changing requirements of the network from a centralized controller. The network administrator can avail of improved network programmability to flexibly control the physical switches from the controller, which runs all the intelligent control and management software, regardless of the vendor or the model of the switches used.
OpenFlow is a widely known protocol for SDN networks that enables the controller to interact with the forwarding plane of the switches and thus make adjustments to the network. The hardware switches can also use OpenFlow messages to inform the controller when a packet arrives with no specified forwarding instructions. The forwarding instructions are based on a flow entry. The controller specifies the set of parameters and how packets that match the flow entry should be processed.
Network control and management
In an IP network, a packet travels from source to destination using a routing table to guide a route. The routing table is dynamically configured using a routing protocol based on traffic condition. Adopting a suitable routing scheme can gain higher network throughput.